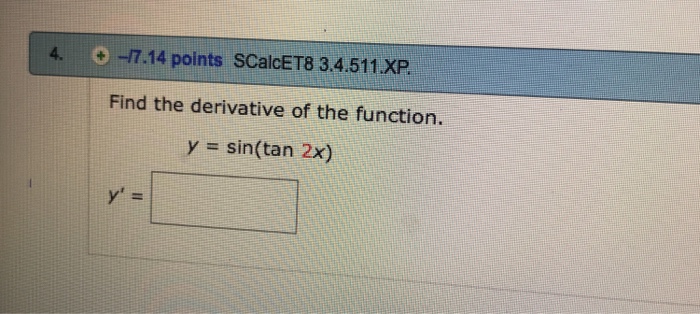
Find the derivative of the functiony = (cos 2x tan x3)9 asked Apr 29, 19 in Mathematics by Toranago technicalmathematics;Apr 16, 15 · About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsQuestion tan 2x Differentiate y = (In x) 8 log, 431 Using rules for derivatives, find the derivative of f(x) sin This question hasn't been solved yet Ask
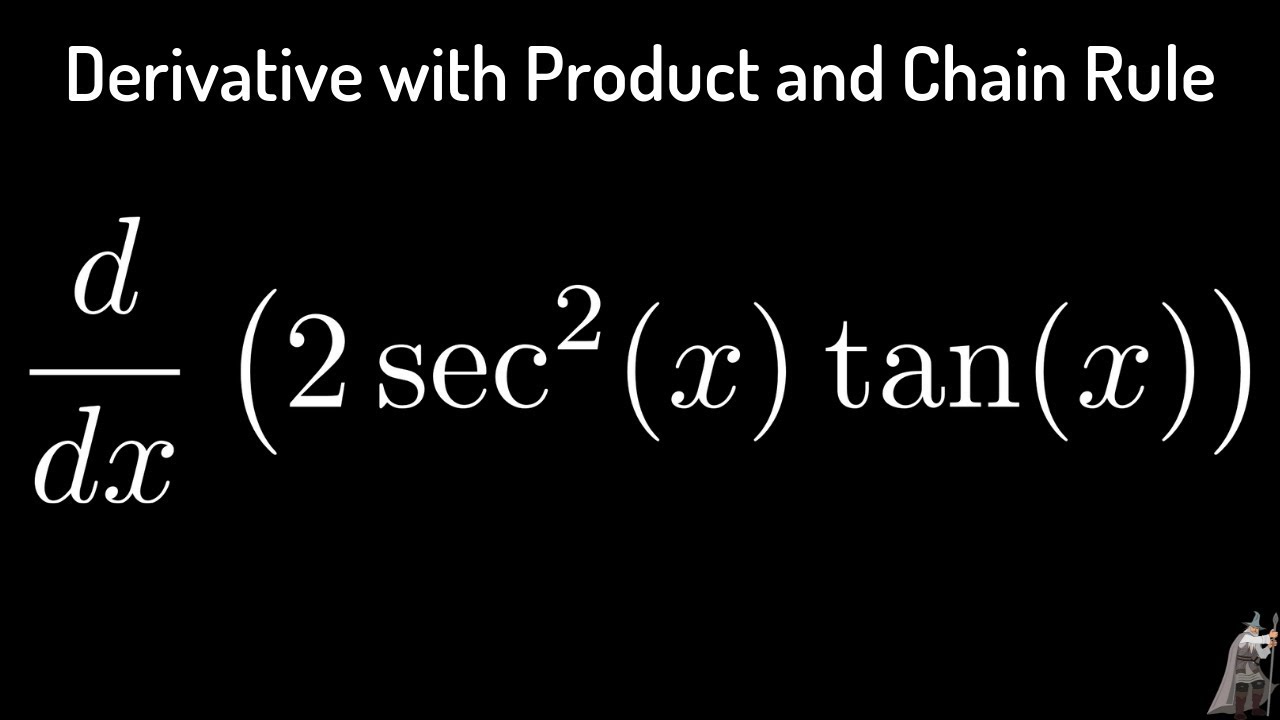
The Derivative Of H X 2 Sec 2 X Tan X Product Rule Example Youtube
Tan(2x+3) derivative
Tan(2x+3) derivative-Definition of Hyperbolic Functions The hyperbolic functions are defined as combinations of the exponential functions \\({e^x}\\) and \\({e^{ – x}}\\) The basicYou could recognize that sec^2x is the derivative of tan x or use a u substitution, let u = tanx (Original post by coconut64) Can anyone explain how to integrate sec^2(x)tanx ?



Chapter 3 Differentiation 1 3 1 The Derivative
Example 16 Calculate the derivative of the function \y = \left( {2 – {x^2}} \right)\cos x 2x\sin x\ at \(x = \pi\)Vx2–1 Vx21 None of the options minimums of the function below are located at y = 2 sin x O None of the options Ox X = 3 Зл 2 2πK, K EZ Ox = 5 2πK, ΚεZ 2x = 10 In order to derive the derivative of the tangent functionApr 13, 21 · Example 22 Find the derivative of tan (2x 3) Let y = tan (2x 3)We need to find derivative of y, ie 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = (𝑑 tan〖(2𝑥3)〗)/𝑑𝑥 = sec2(2x 3) × (𝑑(2𝑥 3))/𝑑𝑥 = sec2 (2x 3) × 2 = 2 sec2 (2x 3) (As (tan x)' = sec2 x) (टीचू) Maths Science
Find the Derivative d/dx y=3tan(2x) Since is constantwith respect to , the derivativeof with respect to is Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that is where and Tap for more steps To apply the Chain Rule, setas The derivativeof with respect to isWe already know the derivatives of sine and cosine we know that the derivative with respect to X of sine of X is equal to cosine of X we know the derivative with respect to X of cosine of X is equal to negative sine of X and so what we want to do in this video is find the derivatives of the other basic trig functions so in particular we know let's figure out what the derivative with respect toThis is very easy, and this involves the use of trig identities math\displaystyle \int \tan ^2\left(x\right)\,dx/math Since math\tan ^2\left(x\right)=1\sec ^2\left(x\right)/math, so we rewrite the equation as math
Apr 16, 21 · The derivative of tan x is sec^2 x Proof of the derivative tan x in easy steps Stepbystep solutions to hundreds of calculus problems, from derivatives to integralsSep 09, 19 · The inverse tangent — known as arctangent or shorthand as arctan, is usually notated as tan1 (some function) To differentiate it quickly, we have two options 1) Use the simple derivative rule 2) Derive the derivative rule, and then apply the rule In this lesson, we show the derivative rule for tan1 (u) and tan1 (x) There are fourDec 14, 18 · That is, the derivative of the function ƒ(x) = e 2x is ƒ'(x) = 2e 2x This derivative tells us the rate of change the output of the original function per change in input Basically, the two equations tell us that the output of the function ƒ(x) = e 2x grows by a factor of 2e 2x per input So if our x value is one, plugging that value into



Derivative Of Tan X Sec X Tan X More



Solved Differentiate Y 1 Sec X Tan X Sec X 1 Sec X Ta Chegg Com
Would the Dy/DX of Sec squared 3x be 3 Sec sqaured 3x 3Tan Squared 3x$\endgroup$ – Another Lonely Cactus Aug ' at 1451 3 $\begingroup$ @HaKuNaMaTaTa amWhy's penultimate step confirms this with the derivative of $\tan^2 x$ $\endgroup$ – fundamentalform Aug ' at 1555Welcome to Sciemce, where you can ask questions and receive answers from other members of the community



Solved Find The Second Derivative Of The Function Y Tan Chegg Com



Derivative Rules For Trigonometric Functions
In this tutorial we shall explore the derivative of inverse trigonometric functions and we shall prove the derivative of tangent inverse Let the function of the form be \y = f\left( x \right) = {\tanY '= ( 2 sin 2x tanx cos 2x sec ^ 2 x) / tan ^ 2 x = (4 sin x cos x (sin x / cos x) (2cos ^ 2 x 1) / cos ^ 2 x)) / tan ^ 2 x = (4 sin ^ 2 x 2 (1 / cosJan 16, 18 · The derivative of tan x is sec 2 x However, there may be more to finding derivatives of tangent In the general case, tan x is the tangent of a function of x, such as tan
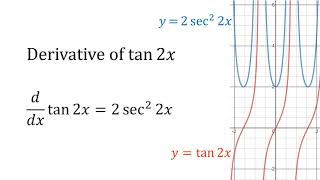


91 Derivative Of Tan 2x Youtube



Differentiate The Following From First Principle Tan2x Youtube
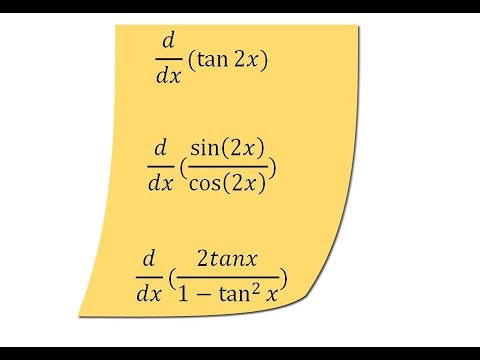
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyGraph of tan x and its Derivative The graphs of \( \tan(x) \) and its derivative are shown below Derivative of the Composite Function tan (u(x)) We now have a composite function which is a function (tan) of another function (u)May 02, 18 · Assuming that you know the derivative rule d dx (tanx) = sec2(x) d dx (tan(2x)) will simply be sec2(2x) ⋅ d dx (2x) according to the chain rule Then d dx (tan(2x)) = 2sec2(2x) If you want to easily understand chain rule, just remember my tips take the normal derivative of the outside (ignoring whatever is inside the parenthesis) and then multiply it by the derivative of the
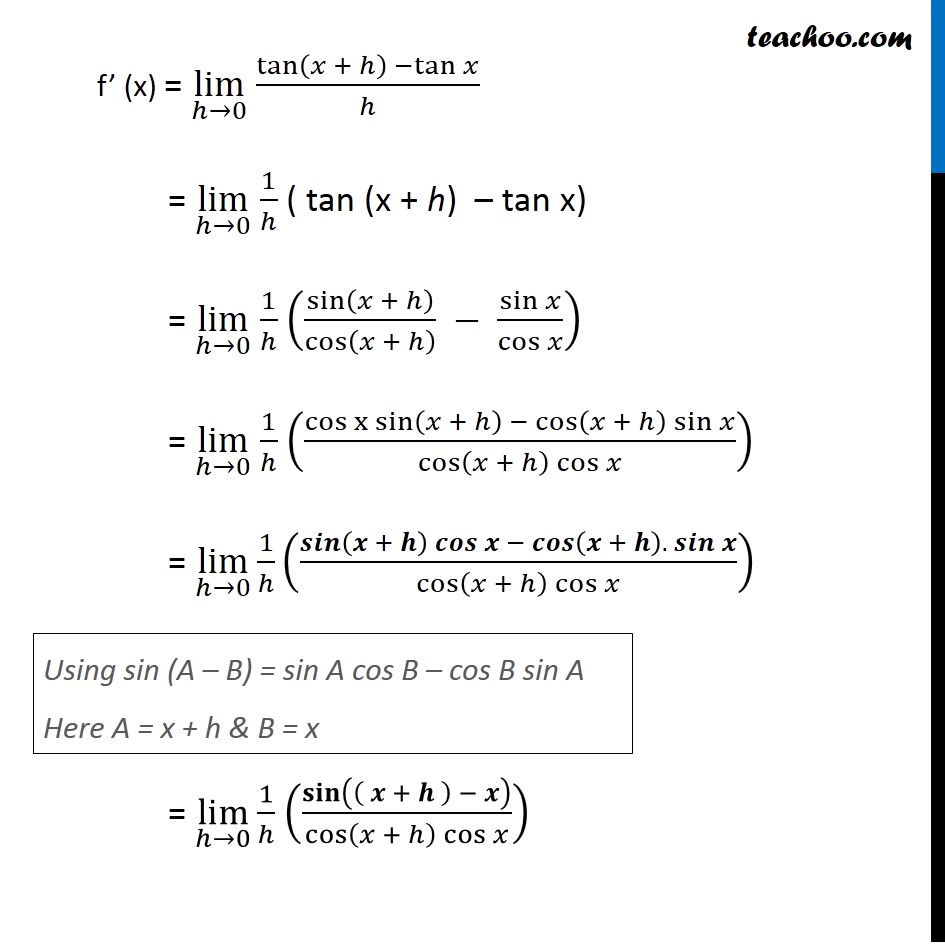


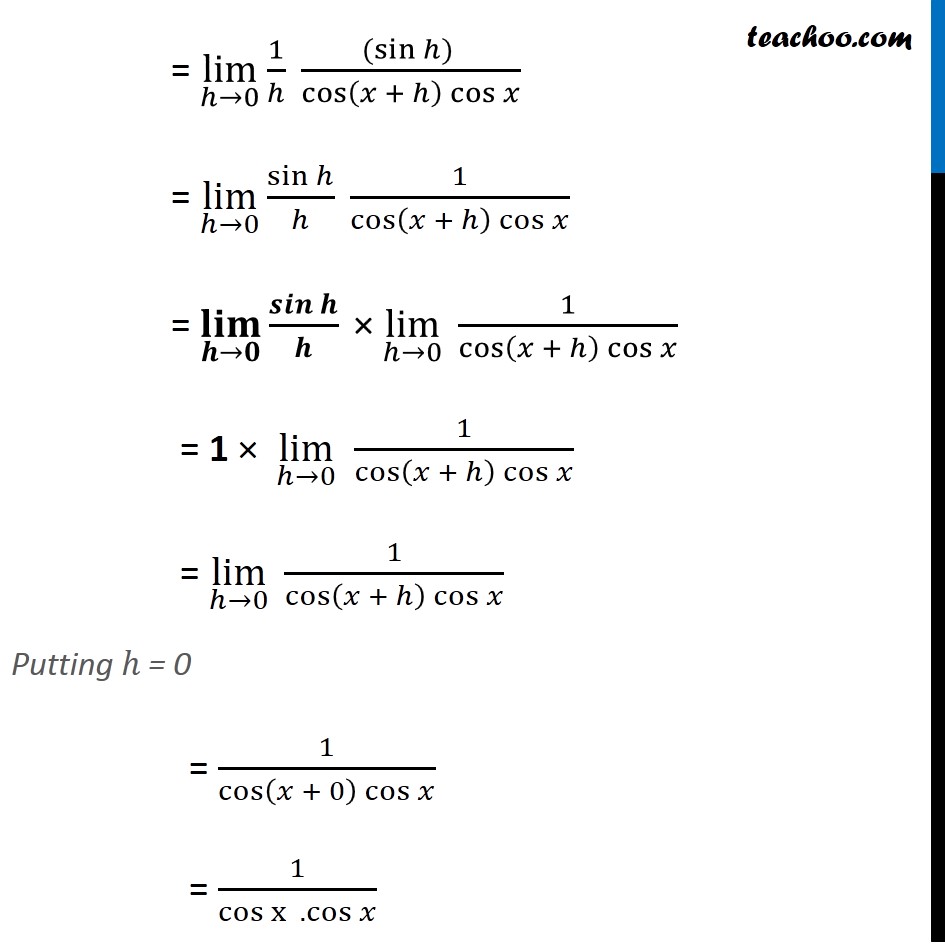
Prove That Derivative Of Tan X Is Sec 2 X By First Principle



Trigonometric Function Differentiation
Derivative of 2tan (2x) (2*tan (2*x))' (2)'*tan (2*x)2* (tan (2*x))' 0*tan (2*x)2* (tan (2*x))' 0*tan (2*x)2* ( (2*x)'/ ( (cos (2*x))^2)) 0*tan (2*x)2* ( ( (2)'*x2* (x)')/ ( (cos (2*x))^2)) 0*tan (2*x)2* ( (0*x2* (x)')/ ( (cos (2*x))^2)) 0*tan (2*x)2* ( (0*x2*1)/ ( (cos (2*x))^2)) 0*tan (2*x)2* (2/ ( (cos (2*x))^2))Eg1 Write sinxcosxtanx as sin(x)cos(x)tan(x) 2 Write secx*tanx as sec(x)*tan(x) 3 Write tanx/sinx as tan(x)/sin(x) 4 Use inv to specify inverse and ln to specify natural log respectively Eg1 Write sin1 x as asin(x) 2 Write ln x as ln(x) 5 Sample Inputs for Practice Eg1 Write (10x2)(x 2) as 10*x2x^2 2 Write cos(x 3) as cos(x^3)$$\tan 2x=\dfrac{2\sin x\cos x}{\cos^2 x\sin^2 x} $$ Furthermore, we express the squares in the denominator as a product (otherwise their derivatives would involve the use of the chain rule),



Leslie Ruo S Blog Rusty Calculus



Solved Question 1 Integrate The Following Function Sec Chegg Com
Jul 26, 15 · Using first principle, the derivative of any function $f(x)$ is given as $$\frac{d(f(x))}{dx}=\lim_{h\to 0}\frac{f(xh)f(x)}{h}$$ Hence, derivative of $\tan^2 x$ is given as $$\frac{d(\tan^2 x)}{dx}=\lim_{h\to 0}\frac{\tan^2(xh)\tan^2(x)}{h}$$ $$=\lim_{h\to 0}\frac{(\tan(xh)\tan(x))(\tan(xh)\tan(x))}{h}$$$$=\lim_{h\to 0}\frac{\tan(xh)\tan(x)}{h}\times \lim_{h\to 0}(\tan(xh)\tanThe derivative of `f(x)=tan(2x pi/2)` is `f'(x) = 2*sec^2(2x pi/2)` and at `x = 3*pi/4` the slope of the tangent is 2 Approved by eNotes Editorial Team Luca B Educator since 11 5,348Given a function , there are many ways to denote the derivative of with respect to The most common ways are and When a derivative is taken times, the notation or is used These are called higherorder derivatives Note for secondorder derivatives, the notation is often used At a point , the derivative is defined to be



The Derivative Of Sec 2 X With Respect To Tan 2 X Is



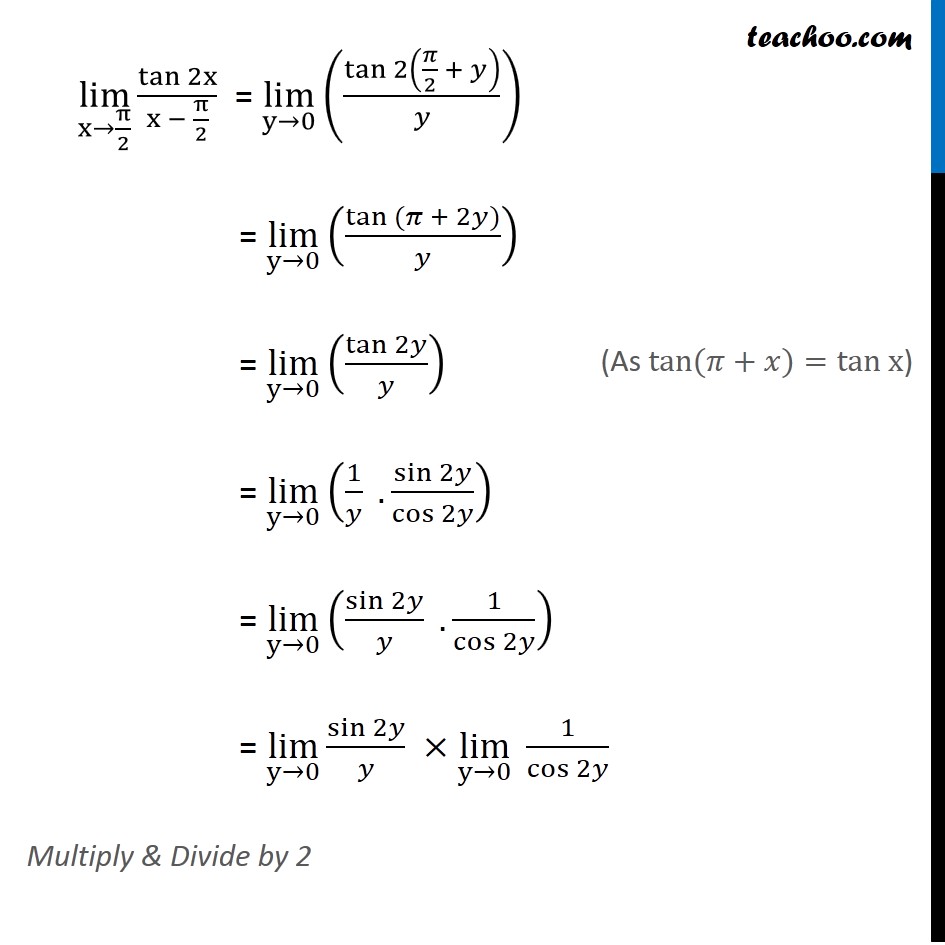
Ex 13 1 22 Lim X Pi 2 Tan 2x X Pi 2 Chapter 13 Class 11
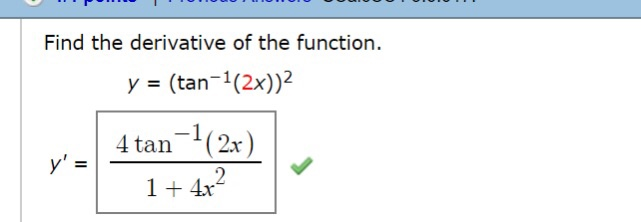
Find the derivative of the functiony = (cos 2x tan x5)4 asked Jun 1, 19 in Mathematics by Gervin calculus;Differentiate Tap for more steps Since 2 2 is constant with respect to x x, the derivative of 2 x 2 x with respect to x x is 2 d d x x 2 d d x x e tan ( 2 x) sec 2 ( 2 x) ( 2 d d x x) e tan ( 2 x) sec 2 ( 2 x) ( 2 d d x x) Move 2 2 to the left of e tan ( 2 x) sec 2 ( 2 x) e tan ( 2 x) sec 2 ( 2 x)Oct 11, 17 · differentiate using the chain rule given y = f (g(x)) then dy dx = f '(g(x)) × g'(x) ← chain rule y = (tanx)2 ⇒ dy dx = 2tanx × d dx (tanx) ⇒ dy dx = 2tanxsec2x Answer link


What Is The Differentiation Of Sec Inverse Tan 2x Quora



Solved Find The Derivative Of The Function Y 6sinh T Chegg Com
Dec 18, 19 · Derivative Of Tangent – The differentiation of trigonometric functions is the mathematical process of finding the derivative of a trigonometric function, or its rate of change with respect to a variable Common trigonometric functions include sin(x), cos(x) and tan(x) For example, the derivative of f(x) = sin(x) is represented as f ′(a) = cos(a) f ′(a) is the rate ofThe derivative of tan 2x is 2 sec 2 (2x) (ie) d/dx tan 2x = 2 sec 2 (2x) Explanation We know that the derivative of tan x is sec 2 x (ie) d/dx (tan x) = sec 2 x According to the chain rule, d/dx tan 2x = sec 2 (2x) d/dx (2x) Therefore, d/dx tan 2x = 2 sec 2 (2x)Tan 2x Differentiate y = (In x) 8 log, 431 Using rules for derivatives, find the derivative of f(x) sin ;



Find Dy Dx 1 Tan 2x 1 Cot 2x Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com
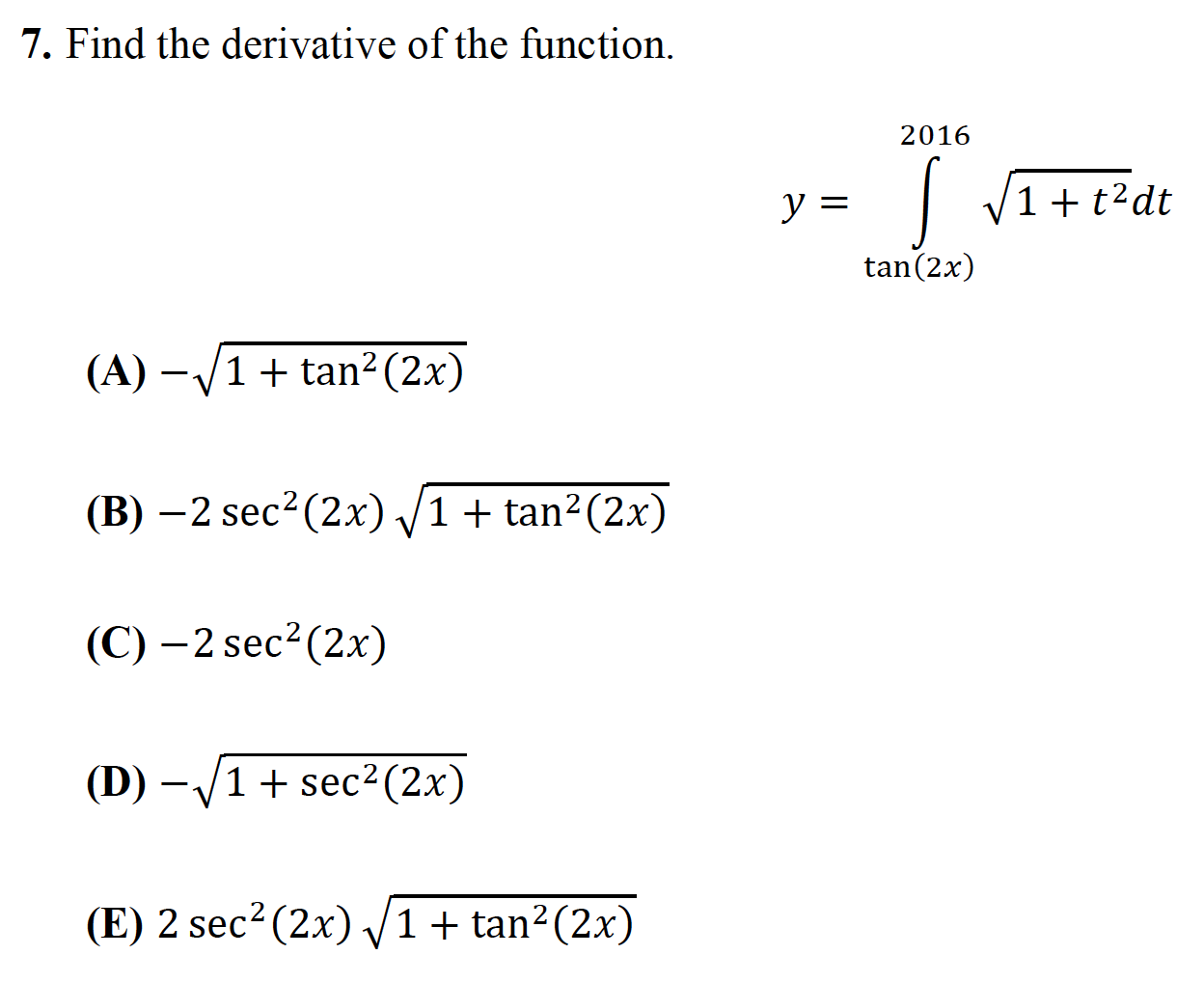


Solved 7 Find The Derivative Of The Function 16 Y 1 Chegg Com
Derivative Calculator computes derivatives of a function with respect to given variable using analytical differentiation and displays a stepbystep solution It allows to draw graphs of the function and its derivatives Calculator supports derivatives up to\\frac{d}{dx} \frac{1}{\tan{x}}\ > Q42 Differentiate Tan 2x 3 Derivative Of Tan 2x 3 Differentiation Of Tan 2x 3 Youtube Find The Derivative Of The Function Y Sin Tan 2x Homework Help And Answers Slader Thanks for the A!Mar 25, · The derivative of tan (2x) is equal to two times the secant squared of two times x Using mathematical notation, the equation is written as d/dx tan (2x) = 2sec^2 (2x) The derivative of tan (2x) can be found by using the quotient rule and the chain ruleThe differentiation of trigonometric functions is the mathematical process of finding the derivative of a trigonometric function, or its rate of change with respect to a variableFor example, the derivative of the sine function is written sin′(a) = cos(a), meaning that the rate of change of sin(x) at a particular angle x = a is given by the cosine of that angle What Is The 2nd Derivative Of Y Tanx Socratic Derivative Of Cos2x By First Principle Prove\\tan^2 (x)\sin^2 (x)=\tan^2 (x)\sin^2 (x) \frac {d} {dx} (\frac {3x9} {2x}) (\sin^2 (\theta))' \sin (1) \lim _ {x\to 0} (x\ln (x)) \int e^x\cos (x)dx \int_ {0}^ {\pi}\sin (x)dx \sum_ {n=0}^ {\infty}\frac {3} {2^n} stepbystepAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsSep 29, · The second derivative of tan^2x is 4sec 2 (x)tan 2 (x) 2sec 4 (x) Interesting property of the derivative of tan^2x It is interesting to note that the derivative of tan 2 x is equal to the derivative of sec 2 x The derivative of > tan 2 x 06 Derivative By Substitution Of Trigonometric Ratio Tan 2 X 3 2tans Tan2x Youtube The Derivative Of H X 2 Sec 2 X Tan X Product Rule Example Youtube Use the graph below to understand why sec 2 (x) gives the slope of tan(x) at any point between ±π/2 (remember that the tangent function is infinite at multiples of ±π/2) Notice that the slope of the tangent function is always positive, and the value of the derivative is always positive, tooStart studying Calculus 1 Derivative Review Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools Derivative of tan sec^2(x) Antiderivative of sec^2(x) tan(x) C Derivative of cotcsc^2(x) Antiderivative of csc^2(x)cot(x) CVx2 – 1 0 3x tan? Find Derivative Of Xsin2x 5 X K X Tan 2x 3 Q 13 X Sin 2x 5x Kx Tan2x3 Maths Limits And Derivatives Meritnation Com Derivative Of Tan 2x Derivative of ln(tan(2x)) (ln(tan(2*x)))' (1/tan(2*x))*(tan(2*x))' (1/tan(2*x))*((2*x)'/((cos(2*x))^2)) (1/tan(2*x))*(((2)'*x2*(x)')/((cos(2*x))^2)) (1/tan(2*x))*((0*x2*(x)')/((cos(2*x))^2)) (1/tan(2*x))*((0*x2*1)/((cos(2*x))^2)) (2/((cos(2*x))^2))/tan(2*x) The calculation above is a derivative of the function f (x)Apr 03, 18 · `(d(sec x))/(dx)=sec x tan x` `(d(cot x))/(dx)=csc^2 x` In words, we would say The derivative of `csc x` is `csc x cot x`, The derivative of `sec x` is `sec x tan x` and The derivative of `cot x` is `csc^2 x` Explore animations of these functions with their derivatives here Differentiation Interactive Applet trigonometric functions#5 Report Thread starter 4 years ago #5 Solved 1 Find The Derivative Of Each Function A E E Chegg Com Derivative Of Arctan X Inverse Tangent Detailed Lesson Nov 12, 19 · The tangent line is the best linear approximation of the function near that input value For this reason, the derivative is often described as the "instantaneous rate of change", the ratio of the instantaneous change in the dependent variable to that of the independent variable The derivative of tan x The derivative of tan x is sec 2 xThanks 0 reply coconut64 Badges 16 Rep?Derivative Calculator computes derivatives of a function with respect to given variable using analytical differentiation and displays a stepbystep solution It allows to draw graphs of the function and its derivatives Calculator supports derivatives up to How To Find The Derivative Of F X Tan 2 3x 2 Quora Solved 5 Now Differentiate The Expression Y Tan 2x With Chegg Com Implicit\derivative\\frac {dy} {dx},\ (xy)^2=xy1 \frac {\partial} {\partial y\partial x} (\sin (x^2y^2)) \frac {\partial } {\partial x} (\sin (x^2y^2)) derivativecalculator \frac {d} {dx}\left (tan^ {2}x\right) en Sign In Sign in with Office365 Sign in with FacebookGet an answer for 'Prove that the derivative of tan x is sec^2 x' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotesAug 19, · $\begingroup$ I think it's more direct than this, as $1tan^2(x)=sec^2(x)$, thanks though!!! Larson Calculus 5 4 52 Find The Derivative Of Y E 2x Tan 2x With The Product Rule Youtube How Do I Integrate Tan 2 X Youtube Nov 02, · From above, we found that the first derivative of tan(2x) = 2sec 2 (2x) So to find the second derivative of tan(2x), we just need to differentiate 2sec 2 (2x) We can use the chain rule to find the derivative of 2sec 2 (2x) (bearing in mind that the derivative of sec^2(x) is 2sec 2 (x)tan(x)) and it gives us a result of 8sec 2 (2x)tan(2x) The second derivative of tan(2x) is 8secJan 30, 13 · Practice Derivatives of tan(x), cot(x), sec(x), and csc(x) Worked example Derivative of sec(3π/2x) using the chain rule Practice Differentiate trigonometric functions Integration Of Inverse Tan 2x Integration By Parts Youtube Derivatives Of Inverse Trigonometric Functions Sin 1 2x Cos 1 X 2 Tan 1 X 2 Sec 1 1 X 2 Youtube Derivative Of Tan 2x 3 From First Principle Brainly In The Derivative Of Tan 1 Sqrt 1 X 2 1 X With Respect To Tan Ex 13 1 22 Lim X Pi 2 Tan 2x X Pi 2 Chapter 13 Class 11 Derivative Of Tan F X Y Web Applications Stack Exchange Answered Calculate The Following Derivative D Bartleby Differentiate The Following From First Principle Tan 2x Differentiate Wrt X Sec 1 1 Tan2x 1 Tan2x Mathematics Topperlearning Com Nti7rxx Finding The Derivative Of Sec 2 X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com Solved Determine The Derivative Fory 10 Tan 2x 9 O A Chegg Com Differentiate The Following By Using First Principle I Tan 2x 1 Ii Tan X Iii Maths Limits And Derivatives Meritnation Com Bestmaths Online Proof 4 Differentiate The Following By Using First Principle I Tan 2x 1 Ii Tan X Iii Maths Limits And Derivatives Meritnation Com Derivative Of Tan 2x Sec 2x What Is The Derivative Of Tan2x Solved Find The Derivative Of The Function Y Sin Tan 2x Chegg Com Solved 2 Use The Chain Rule To Find The Derivative Of F Chegg Com Solved 00 X Tan 2x 6 Find The First Derivative Of The Chegg Com Differentiate Each Of The Following From First Principle Tan 2x Find The Derivative Of Tan 2x 3 Solved Differentiate The Following Function With Respect Chegg Com The Derivative Of Tan 2x W R T Cos 2x Is Maths Limits And Derivatives Meritnation Com Chapter 3 Differentiation 1 3 1 The Derivative Solved Find The Derivative Of The Function X Tan 2x Chegg Com Find The Derivative Of Y Tan 2x At X P Youtube Misc 25 Find Derivative X Cos X X Tan X Miscellaneous Derivative Of Tan2x Sin2x Cos2x And 2tanx 1 Tan 2x Youtube Differentiate The Following From First Principles I Tan 2 X Ii Tan 2x 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community Derivative Of Tan Inverse With Chain Rule Youtube The Derivative Of Tan X Is Sec 2 X Why Mathematics Stack Exchange Differentiation Of Tanx 2 Youtube Second Derivative Of Tan 2x Youtube Ap Calculus Ab How Do I Find The Derivative Of The Trig Function Of A Trig Function Y Sin Tan2x Homeworkhelp Solved 7 46 Find The Derivative Of The Function 13 Y Co Chegg Com Ex 13 1 22 Lim X Pi 2 Tan 2x X Pi 2 Chapter 13 Class 11 Find The Derivative Of The Function Tan 2x 3 From The Definition First Principles Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community Ii F Find Derivative Of Tan 2x At X Pi 6 Youtube Example 22 Find Derivative Of Tan 2x 3 Chapter 5 Class 12 Question Video Differentiating Trigonometric Functions Nagwa How Do You Calculate Derivative Of Sec 2 X The Student Room Differentiation Of Tan 2 X And X 3 X 4 Youtube Prove That Derivative Of Tan X Is Sec 2 X By First Principle 05 Derivative Of Tangent Function Tan2x And Tanx 2 Youtube Derivative Of Tan X Sec X Tan X More Derivative Of Tan 2x 3 F 2tanx 1 Tan 2x Cos2x 1 Sec 2x 2tanx 2 Tan2x ただの悪魔の画像 Derivatives Of Trigonometric Functions Differentiating Trigonometric Functions Review Article Khan Academy Solved Compute The Derivative Of The Function F X Tan Chegg Com Finding The Derivative Of Sec 2 X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com Answered Find The Derivative F X E Tan 2x Bartleby Solved A Differentiate The Following Function With Resp Chegg Com Differentiate The Following Function Tan 2x Find The Derivative Of The Given Function Y Tan 2x 1 Cot 2x I Tried Converting The Original Function In Terms Of Sin And Cos But It Was Still Too Complicated To Be Called Simplified Brandi S Buzzar Blog Proof Derivative Tan X Sec 2 X The Derivative Of Tan 2x Derivativeit Differentiate The Following From First Principle Tan 2x 1 Derivative Of Tan X Sec X Tan X More The Derivative Of Cos 3x Derivativeit Theo Flore Lire Livres Gratuits Telecharger Ebooks If Y Tan X Tan 2x Tan 3x Then Dy Dx Equals Prove That Derivative Of Tan X Is Sec 2 X By First Principle Clicker Question 1 What Is The Derivative Of F X 7x 4 E X Sin X A 28x 3 E X Cos X B 28x 3 E X Cos X Find Derivative Of Tan Square X By First Principle Maths Limits And Derivatives Meritnation Com Solved Q 4 Find The Derivative Of F X X Tan 2x Q 5 F Chegg Com What Is The Formula Of Tan2x Quora Solved Find The Derivative 29 Y 8 10 Secx A Y 1 Chegg Com What Is The Derivative Of Sec 2 Tan 1 X With Respect Ex 1 First And Second Derivatives Using The Chain Rule F X Tan 2x Youtube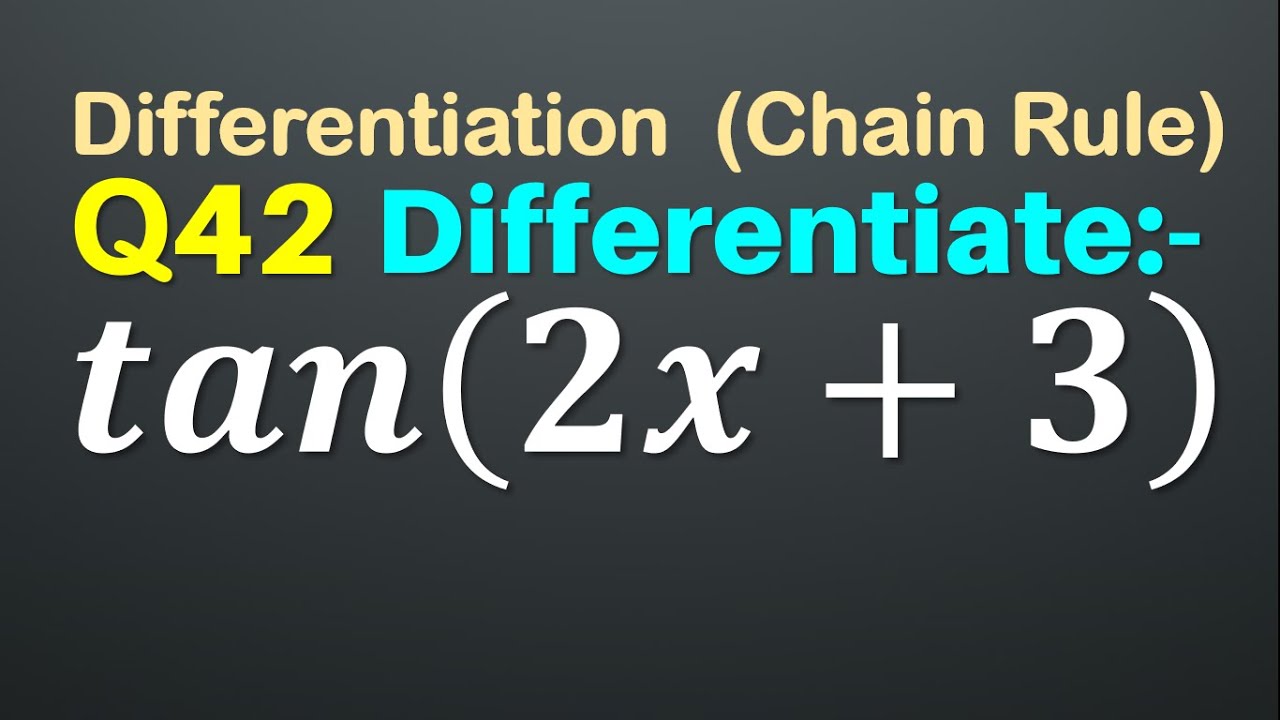











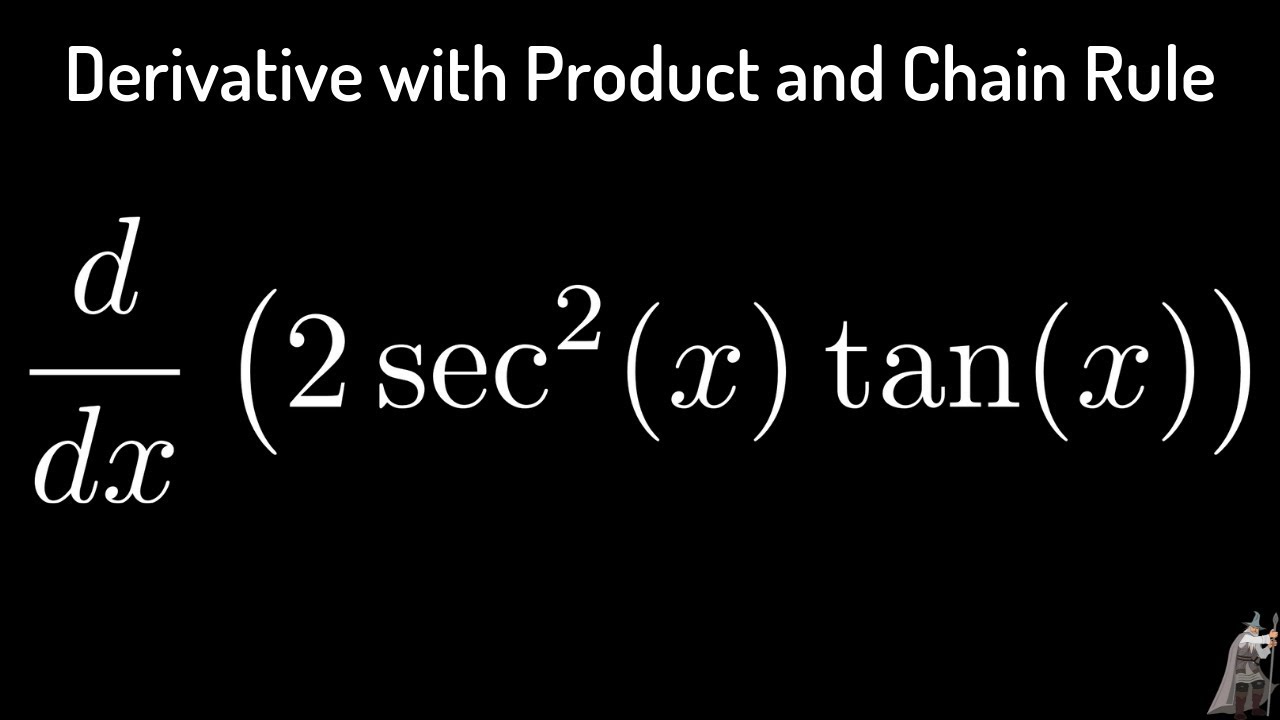

























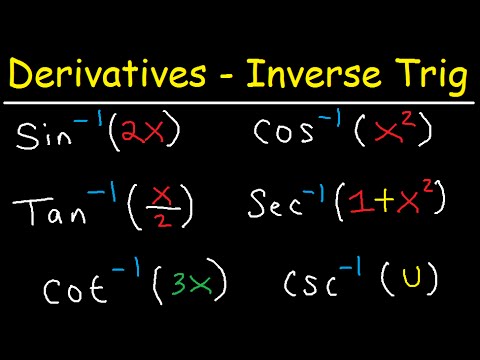





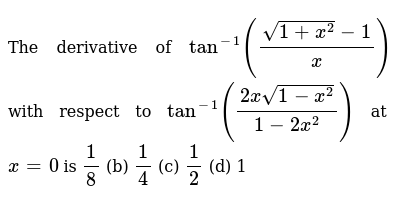


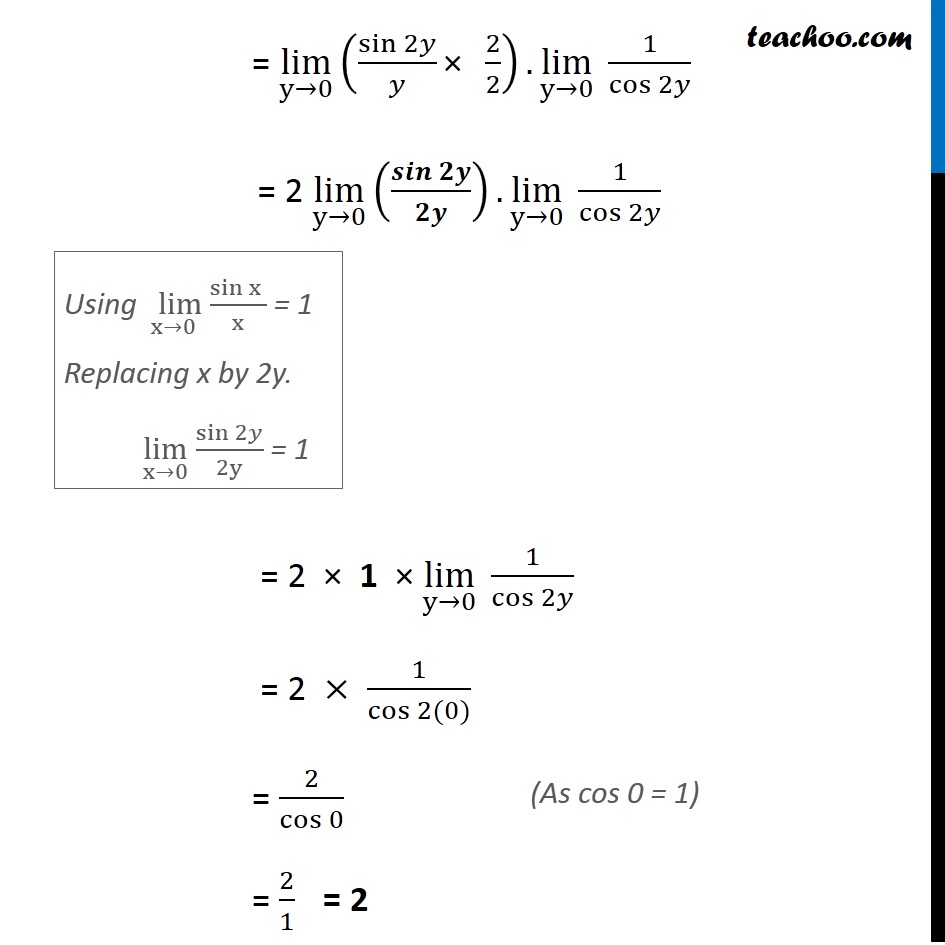





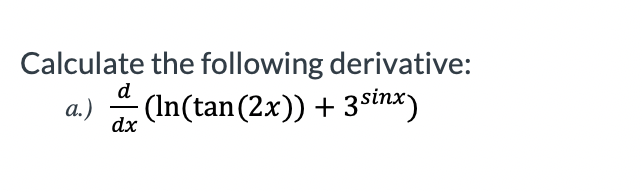





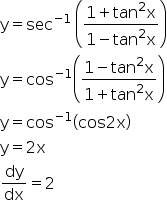





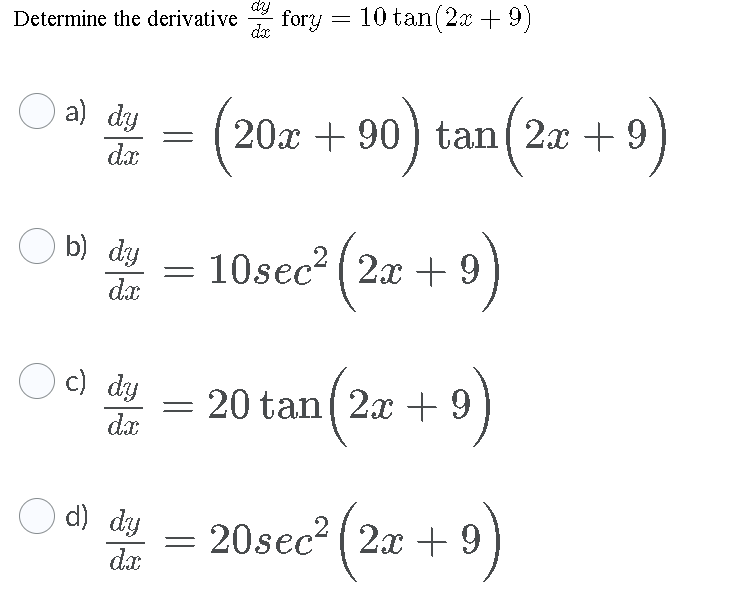







































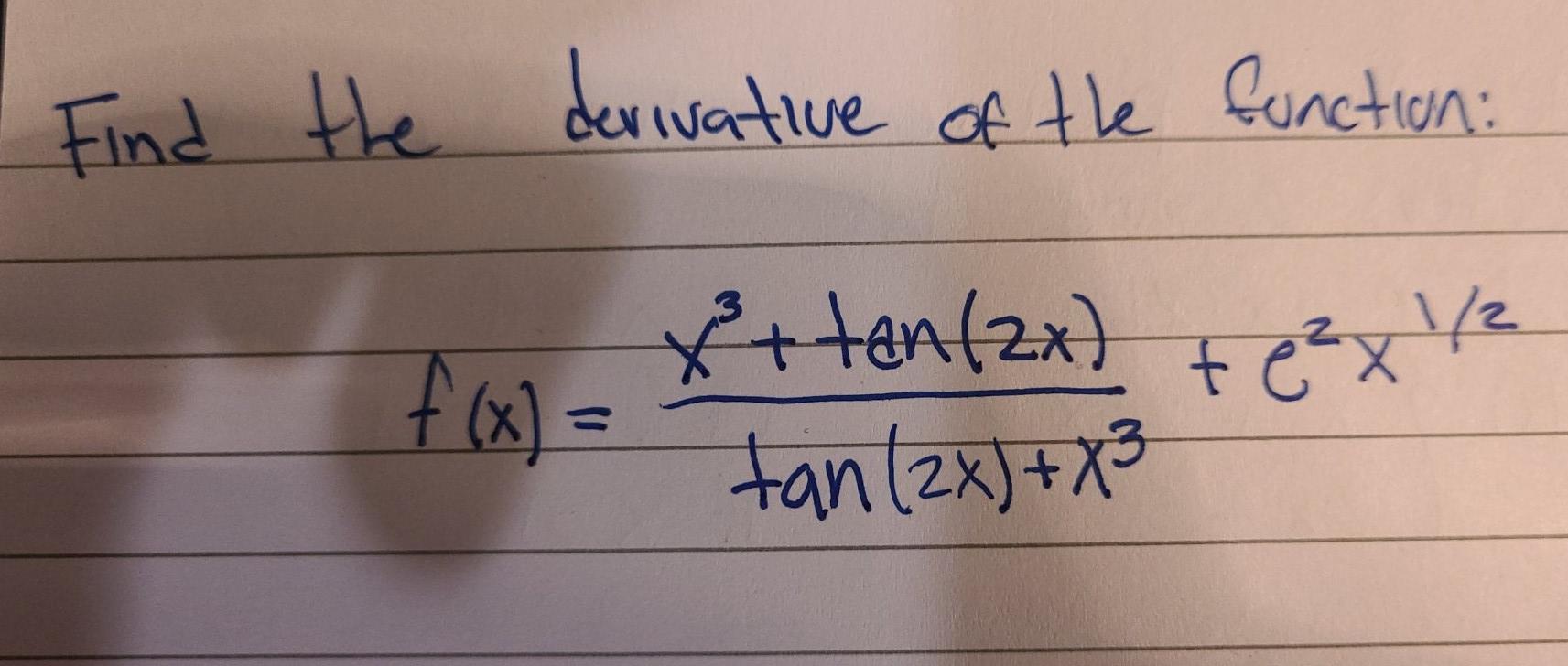


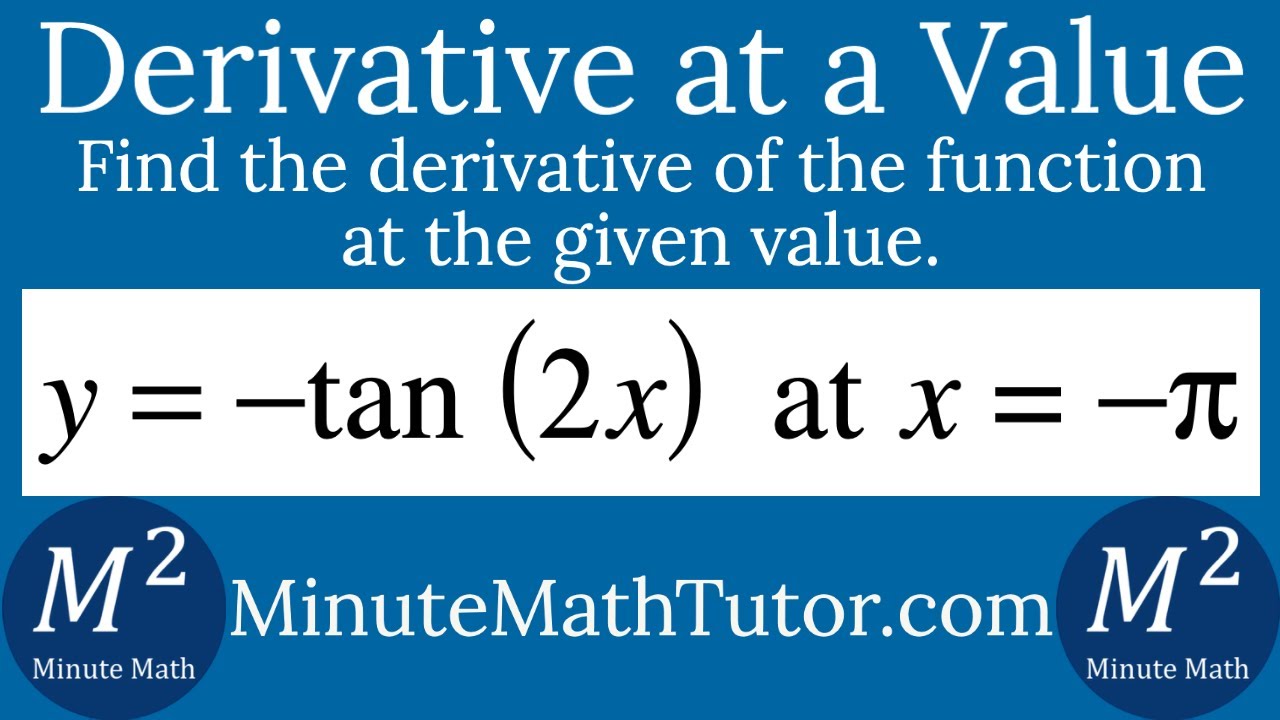





























































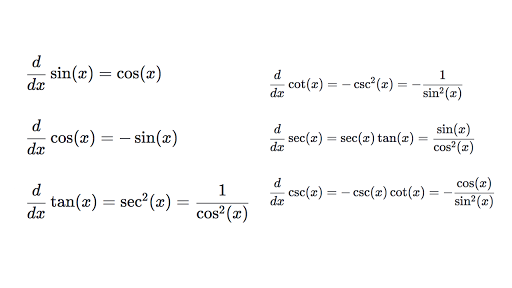


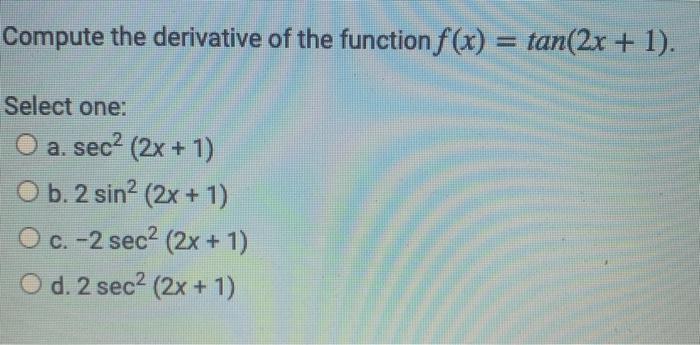





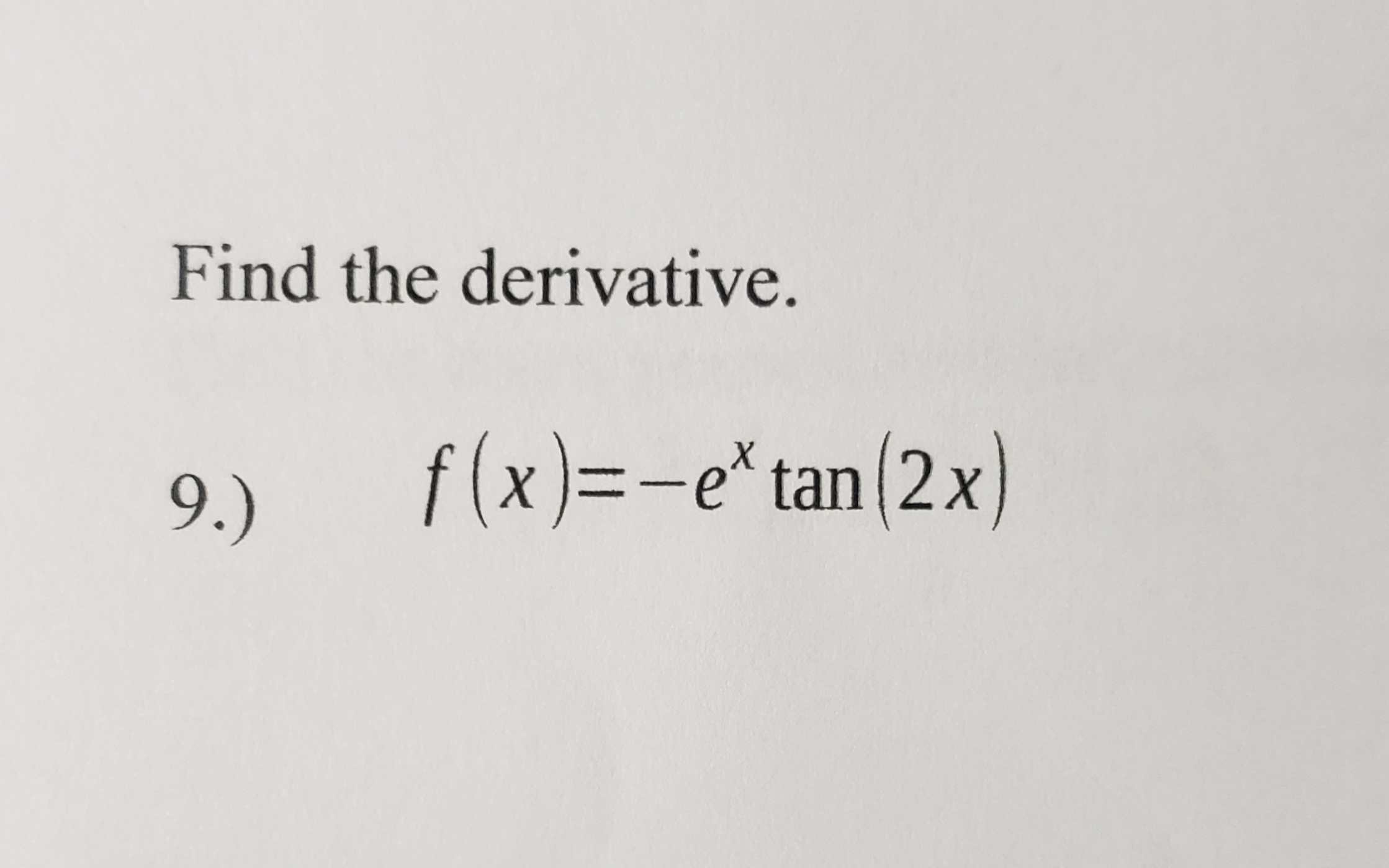

















































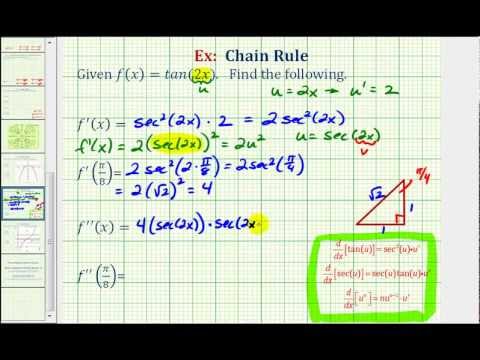





0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿